Intelligent Agents
What is an agent?
An agent is basically an individual or entity that is capable of perceiving the world through sensors and reacting to it through the use of actuators. In other words, each input taken in by an agent will have a reaction
The process of an agent reacting to an input it gets from the environment is known as a perception - action cycle as demonstrated below:
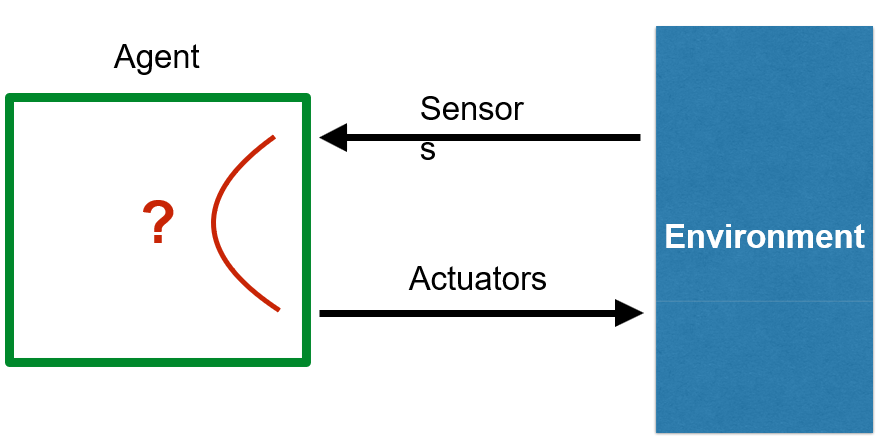
The most common type of agent is known as a rational agent, an agent that acts on behalf of a system to achieve the best outcome. In other words:
- A rational agent is an agent said to have artificial intelligence integrated into it
- It can interpret data, store it and then learn from it
- Hence, adapting to the data it learned from
When designing a rational agent, a PEAS approach may be regarded.
PEAS stands for Performance, Environment, Actuators and Sensors. It is a metric or rather method referred to in listing out the mentioned features and properties of an agent and its environment.
- Performance - evaluates the goal to be achieved/assessed by the system (e.g. fuel efficiency)
- Environment - Defines the task environment in which the agent acts
- Actuators - Means taken for an agent to react to its environment
- Sensors - Means taken to perceive the environment for the agent (e.g infra-red sensor)
What are the different types of Task Environments?
There are different kinds of task environments that infer different influences onto an agent such that they affect the way they may behave:
| Task Environmnet | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Observable | This is an environment where all the factors of it are available to the agent present in it it at any given time | e.g. Chess Board |
| Partially-Observable | A partially observable environment is where only a portion of the environment is perceivable by the agents sensors making it such that the environment may be too noisy for the agent to understand | e.g. A game of poker where the player can (is allowed to) see only their cards |
| Deterministic | This describes a task environment that states that the outcome of any move on it will be predictable with certainty | e.g. Solving a math problem, the solution is always there with certainty |
| Stochastic | The outcome of an agents move/interaction in an environment as such is uncertain due to their being instances of probability and randomness | e.g. Rolling a dice in any game makes it a stochastic environment |
| Static | In this environment, if an agent does not make any interactions the environment will not change as the agent is deciding | e.g. Crossword Puzzle |
| Dynamic | In this environment, while the agent is deciding, the environment will change around them such that it may influence the course of their next actions | e.g. Stock Market trading bot, nothing can stop stock price fluctuations even when the bot is deciding |
| Discrete | The environment will only ever have a finite number of possible actions in it | e.g. Crossword Puzzle, Chess, Checkers |
| Continuous | This environment will have an uncountable number of moves and interactions that may be infinite | e.g. Autonomous arm moving in a three-dimensional space |
| Single-agent | Only one agent is present in the environment | e.g. Robotic arm or vacuum cleaner robot |
| Multi-agent | Multiple agents present in the environment | e.g. Chess pieces on a chess board |
| Episodic | Each action that takes place in this sort of environment, does not influence something that could happen in the future, hence the name episodic as each move does not affect the future | e.g. Spam email detection, each spam email is classified separately |
| Sequential | Actions in this environment influence future states and decisions, hence making each move dependant on the previous move | e.g. A game of chess |
| Benign | The environment here has no objective to go against what you wish such that it will not affect the outcome of an agent. Think of it as an environment that is free from external threats and factors that may potentially affect the performance of the agent in it | e.g. A virtual environment in a code (.venv) where all the dependencies are present in the mentioned environment while not being affected by any of the external (base) dependencies |
| Adversarial | In this environment, external factors will affect the outcome of the agent as it presents an opposition to the agent. In other words, the environment observes you and tries to contradict every decision you make | e.g. A game of chess, checkers, etc |
| Known | The agent understands the rules and consequences of actions | e.g. Solving a maze where the map is available or a search algorithm with knowledge of the entire maze |
| Unknown | The agent must learn the rules and consequences through exploration | e.g. Depth first, breadth first search |
Now, there are multiple types of agents to be considered, refer to the following sub-section:
Types of Agents
The different types of agents include Simple Reflex, Model Based Reflex, Goal Based, Utility Based, learning agents, each of which has different features to them
Simple Reflex Agents
- Simple agent that acts on a condition action rule
- If it interacts with the environment and gets an input it then reacts to it
- It acts based only on its current percept's and does not consider past percept's
- Advantages
- Simple, quick and east to implement
- Disadvantages
- Environment must be fully observable or else it will get stuck at a point
- Since it cannot have a percept history it is not intelligent
Model Based Reflex Agents
- Simple agent that can maintain an internal state which contains data from past percept's
- Ideal for handling partially observable environments (e.g. Take Wumpus world for example, here the agent may store percept's of stenches and smells)
- Advantages
- Can work in partially observable environments
- Disadvantages
- Cannot model the world accurately and reliably
Goal Based Agents
- Extension of model based reflex agents, except now its capable of retaining goal values
- This incentivises the agent to optimize its algorithm when trying to achieve a goal
- Decisions will be based off heuristics (distances from current node to goal node)
- Actions will always reduce current distance of state to goal
- Advantages
- Flexible
- Disadvantages
- Needs searching and planning
Utility Based Agents
- Extension of a goal based agent where instead of just considering how it can efficiently achieve a goal, it also considers the agents satisfaction
- Ensures that utility values per node are high as well (e.g. Comfort of current state)
- Advantages
- Can solve and sort through conflicting goals
- Disadvantages
- Due to the utility function, sometimes reaching the goals states path may be inefficient
Learning Agents
- Basically an agent that has an artificial intelligence integrated into it, hence enabling the agent to infer rational choices from past percept's
- The agent can learn from past percept's and make optimal decisions based on them (such as making a move that is common, etc)
- Each move is given performance feedback based on how much of an effect it has
- These critics are what motivate the agent to do better and then utilize better paths and options by learning from them