Apache Airflow
What is Apache Airflow?
Airflow is simply an open source batch oriented automation/orchestrating tool for tasks and data streams that enable programs to be carried out as a continuous process. Workflows are monitored as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG's). Airflow is primarily used for monitoring ETL processes, data pipelines, and machine learning workflows in a scalable and efficient manner
In other words, Airflow is a tool used to orchestrate and author schedules based tasks and algorithms that monitor workflows. Some of its key use cases include:
- Ideal for monitoring data pipelines and scheduling recursive tasks in it
- Machine learning model training (e.g. when new data is collected it is fed into the model)
- Automated generation of reports
- Backups and other similar Devops tasks
Airflow considers and processes workloads through DAG's, which is a subclass of Airflow's basic operators:
- Operators - Predefined tasks that can be strung together quickly
- Sensors - Type of operator that waits for an external event to occur
- TaskFlow - A custom python package that operates as a task with the decoration
@task
Airflow's Architecture
The Airflow platform lets you build and run workflows, which are represented as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). A sample DAG is shown in the diagram below.
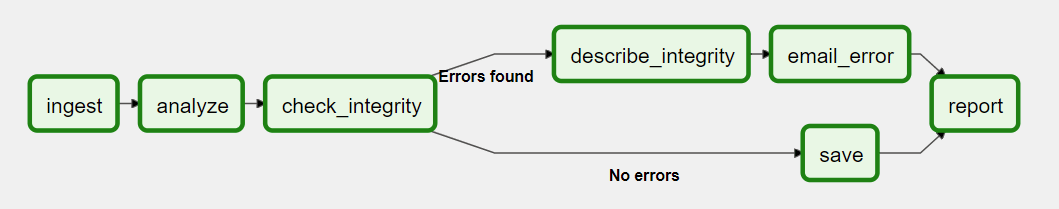
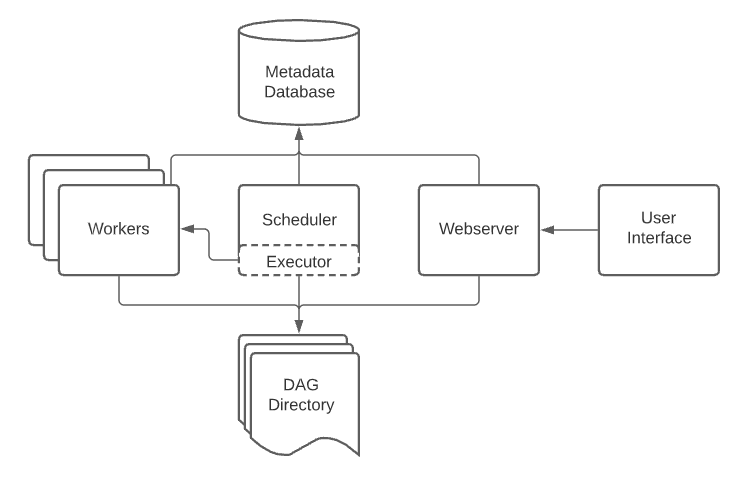
A DAG contains tasks (action items) and specifies the dependencies between them and the order in which they are executed. A Scheduler handles scheduled workflows and submits Tasks to the Executor, which runs them. The Executor pushes tasks to workers.
Other typical components of an Airflow architecture include a database to store state metadata, a web server used to inspect and debug Tasks and DAGs, and a folder containing the DAG files.
What is a DAG?
A DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, it is simply a collection of tasks put together in an ordered manner using directed edges and nodes that represent tasks. A DAG defines the order in which these tasks should be executed, inclusive of any dependencies that may be there between each task (node)
The main feature and point of a DAG is the fact that it does not recur as it goes in one direction, this means that once one task is finished earlier it moves into the next and cannot revert back into the previous task.
Each edge in a DAG is known as a "directed dependency", hence stating that each relationship/edge between nodes can specify how they depend on each other.
Here are some important terminologies you should understand:
- Operators - Task in DAG, defines a single task in a data pipeline, DAG or workflow